Labor rate variance The labor rate variance occurs when the average rate of pay is higher or lower than the standard cost to produce a product or complete a process. With either of these formulas, the actual quantity used refers to the actual amount of materials used to create one unit of product. If there is no difference between the standard price and the actual price paid, the outcome will be zero, and no price variance exists. As demonstrated in this chapter, standard costs and variance analysis are tools used to project manufacturing product costs and evaluate production performance. Standard costs variance analysis is used to determine the variances between the standard amounts projected for manufacturing costs and the actual amounts incurred.
- Management has requested standard cost variances in order to isolate the issue.
- As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider using cheaper materials, changing suppliers, or increasing prices to cover costs.
- Any variance between the standard costs allowed and the actual costs incurred is caused by a difference in efficiency or a difference in rate.
- Management can then compare the predicted use of 600 tablespoons of butter to the actual amount used.
- Examples of typical overhead costs are production facility electricity, warehouse rent, and depreciation of equipment.
Manufacturing Overhead
Actual manufacturing data are collected after the period under consideration is finished. Actual data includes the exact number of units produced during the period and the actual costs incurred. The actual costs and quantities incurred for direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead are reported in Exhibit 8-1. The unfavorable labor rate variance is not necessarily caused by paying employees more wages than they are entitled to receive. Favorable rate variances, on the other hand, could be caused by using less-skilled, cheaper labor in the production process.
Ethical Job Order Costing
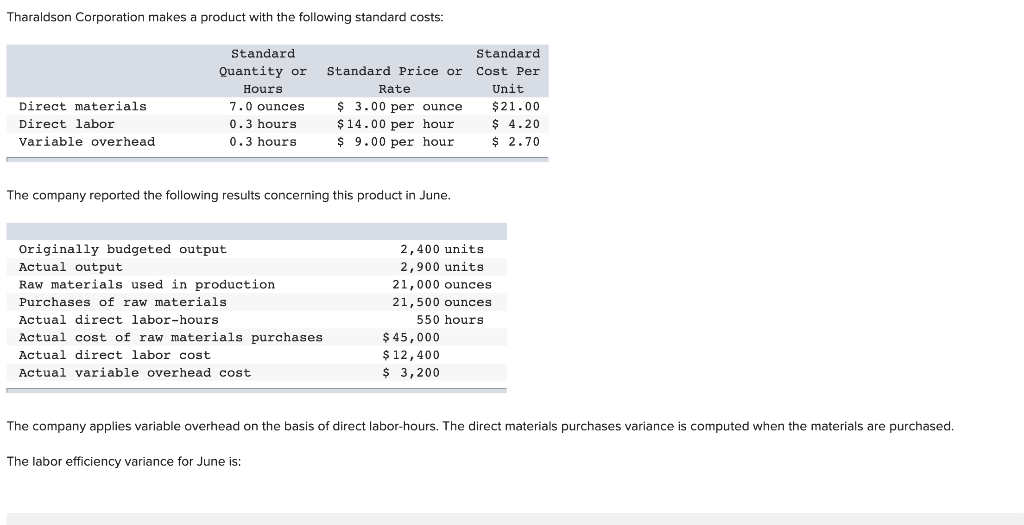
During the period, Brad projected he should pay $675,000 for direct labor to produce 150,000 units. As mentioned previously, standard rates and quantities are established for variable manufacturing overhead. When discussing variable manufacturing overhead, price is referred to as rate, and quantity is referred to as efficiency.
Total variable manufacturing costs variance
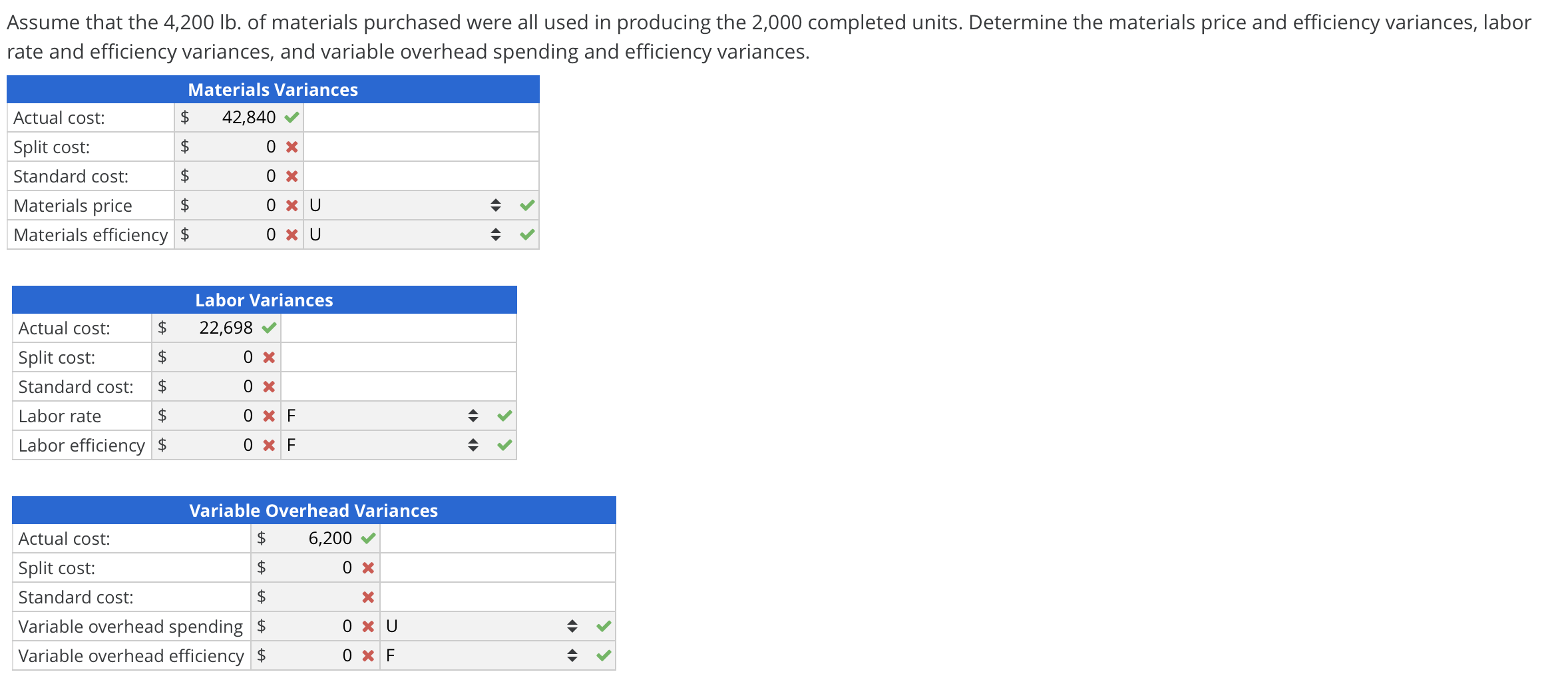
The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the direct materials quantity and price variances. The direct materials quantity and price variances are used to determine if the overall variance is a quantity issue, price issue, or both. Standards for variable manufacturing costs include both quantity and price standards. The quantity standard establishes how much of an input is needed to make a product or provide a service. These standards can be used to make financial projections and to evaluate performance by comparing the standards to actual performance at the end of the period. Any discrepancy between the standard and actual costs is known as a variance.
Managerial Accounting
It is the accountant’s job to ensure that the amounts recorded in the accounting system fairly represent the economic activity of the company, and the fair and proper allocation of costs. When both administrative and production activities occur in a common building, the production and period costs would be allocated in some predetermined manner. These costs are necessary for production but not efficient to assign to individual product production.
What may be a direct labor cost for one company may be an indirect labor cost for another company or even for another department within the same company. If the employee’s work can be directly tied to the product, it is direct labor. If it is tied to the factory but not to the product, it is indirect labor. If it is tied to the marketing department, it is a sales and administrative expense, and not included in the cost of the product. When Dinosaur Vinyl requests materials to complete Job MAC001, the materials are moved from raw materials inventory to work in process inventory. We will use the beginning inventory balances in the accounts that were provided earlier in the example.
Typically, the hours of labor employed are more likely to be under management’s control than the rates that are paid. For this reason, labor efficiency variances are generally watched more closely than labor rate variances. Labor efficiency variance Usually, the company’s engineering department sets the standard amount of direct labor-hours needed to complete a product.
The primary focus on costs allows some leeway in recording amounts because the accountant assigns the costs. When jobs are billed on a cost-plus-fee basis, management may be tempted to overcharge the cost of the job. Cost-based contracts may include a guaranteed maximum, time and materials, or cost reimbursable contract. The training company may charge for the hours worked by instructors in preparation and delivery of the course, plus a fee for the course materials. In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is 0.20 pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the standard quantity used is 0.25 pounds.
Kitchen Co. is experiencing production problems with SuddyBuddy, its most profitable product. Management has requested standard cost variances in order to isolate the issue. Standard and actual manufacturing cost data for SuddyBuddy are provided below. The standard quantity and price to make one unit of Lastlock are provided below. One major issue in all of these contracts is adding too much overhead cost and fraudulent invoicing for unused materials or unperformed work by subcontractors. Management might be tempted to direct the accountant to avoid the appearance of going over the original estimate by manipulating job order costing.
The materials price variance of $ 6,000 is considered favorable since the materials were acquired for a price less than the standard price. If the actual price paid per unit of material is lower than the standard price per unit, the variance will be a favorable variance. A favorable outcome means actual quantity is the actual direct material or direct labor used to manufacture the you spent less on the purchase of materials than you anticipated. If, however, the actual price paid per unit of material is greater than the standard price per unit, the variance will be unfavorable. An unfavorable outcome means you spent more on the purchase of materials than you anticipated.
This is unfavorable because they actually spent more per unit than the standards allowed. The materials price variance of $ 6,000 is considered favorable since the materials were acquired for a price less than the standard price. If the actual price had exceeded the standard price, the variance would be unfavorable because the costs incurred would have exceeded the standard price. We do not show variances with a negative or positive but at the absolute value with favorable or unfavorable specified.
Leave a Reply